AI Overview
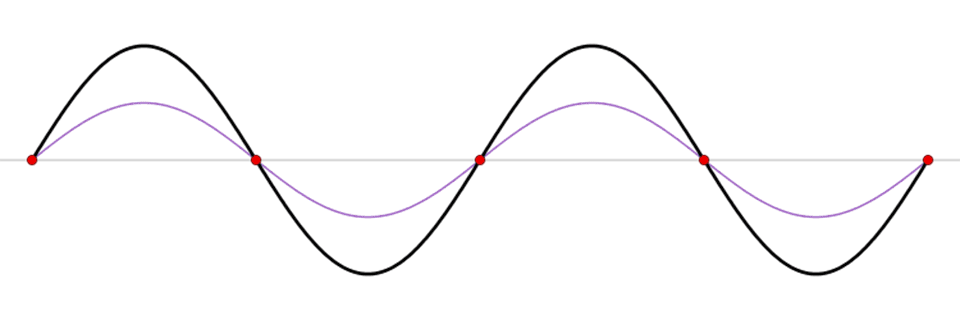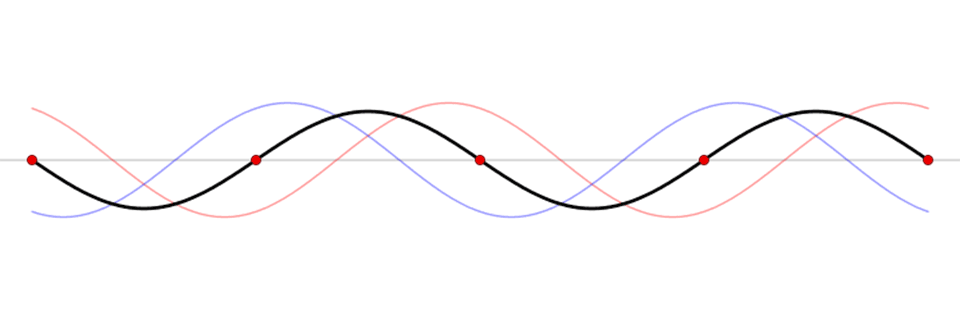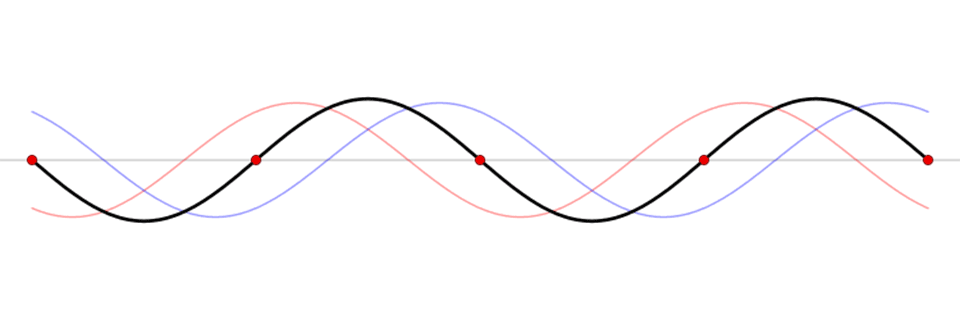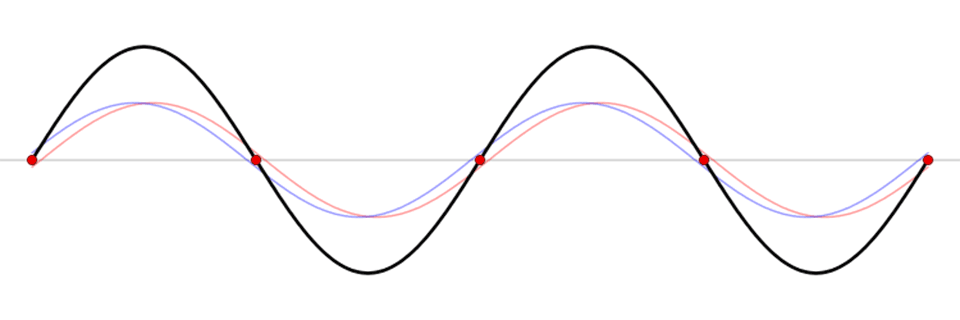
A seiche is a standing wave in an enclosed or partially enclosed body of water, caused by disturbances like strong winds, earthquakes, or atmospheric pressure changes. It's like a sloshing motion, similar to water in a bathtub, where water is pushed to one end and then oscillates back and forth. These events can cause dramatic changes in water levels, with the water level dropping significantly at one end of the lake and rising sharply at the other.
What causes a seiche?
- Wind: Strong, persistent winds pushing water to one side of the lake are the most common cause.
- Earthquakes: Seismic activity can cause the water to slosh back and forth.
- Atmospheric pressure: Rapid changes in air pressure can also generate seiches.
- Other factors: Landslides, heavy rains, and changes in water density can also contribute.
What are the effects of a seiche?
- Water level changes: A seiche can cause a dramatic difference in water levels between different ends of a lake, with one area experiencing flooding and another seeing shorelines exposed.
- Dangerous waves: While many are not dangerous, some seiches can create powerful waves that can sweep people off piers, sink ships, or damage shorelines.
- Damage: The rising water can lead to flooding and, when combined with ice, can cause ice to be thrown onto the shore, causing damage.
- Ice damage: If there is ice on the water, waves can throw it against the shore, causing damage.